Learning to play the violin starts with understanding its parts, mastering the correct posture, developing a proper bow hold, and getting familiar with basic music notation. Follow these clear, step-by-step instructions to build a strong foundation.
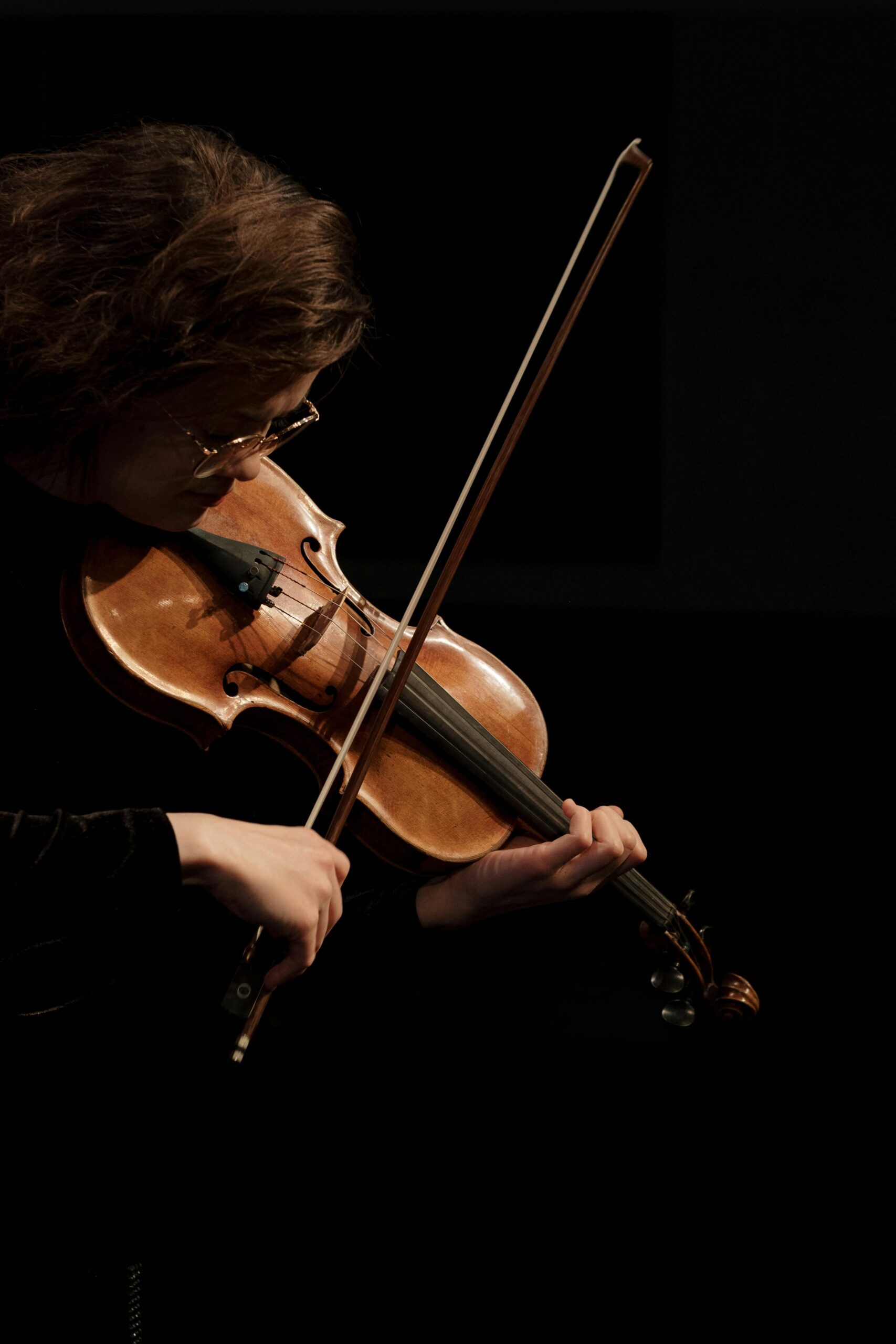

Learn the Basics of Playing Violin
Understand the Parts of a Violin
To play the violin well, you need to know its main parts:
- Body: The main wooden part, which includes the top, back, and sides.
- Neck: The long piece that extends from the body and supports the fingerboard.
- Fingerboard: The smooth, black surface on the neck where you place your fingers.
- Pegs: Used to tune the strings.
- Bridge: Supports the strings and transfers vibrations to the body.
- Strings: Usually four, tuned to G, D, A, and E.
- Bow: A stick with horsehair, used to produce sound by rubbing the strings.
- Tailpiece: Holds the strings at the bottom end.
- Chinrest: Provides a comfortable place for your chin.
Master the Correct Violin Holding Posture
Proper posture is crucial for playing the violin comfortably and effectively. Follow these steps to ensure you’re holding your violin correctly:
- Stand or Sit Upright: Keep your back straight and relaxed.
- Hold the Violin on Your Left Shoulder: Rest the violin on your left shoulder, with the chinrest under your jaw.
- Align the Violin with Your Shoulder: The violin should be parallel to the floor and aligned with your shoulder.
- Support with Your Left Hand: Gently support the neck of the violin with your left hand, fingers curved and relaxed.
- Rest Your Chin on the Chinrest: Place your chin on the chinrest, keeping your head straight and relaxed.
Develop Proper Bow Hold and Technique
A good bow hold is essential for producing a clear sound. Here’s how to hold and use the bow correctly:
- Hold the Bow with Your Right Hand: Position your thumb under the frog (the thick end of the bow) and your fingers on top.
- Curve Your Fingers Naturally: Your index finger should rest on the bow stick, while the middle and ring fingers lightly curve around it.
- Place Your Pinky on Top: Rest your pinky on the top of the bow, slightly curved.
- Keep Your Hand Relaxed: Ensure your hand is relaxed to avoid tension.
To develop good technique, practice these bowing exercises:
- Straight Bows: Draw the bow straight across the strings, keeping it parallel to the bridge.
- Long and Short Strokes: Practice alternating long, smooth strokes with short, quick strokes.
- Even Pressure: Apply consistent pressure with your index finger to produce an even sound.
Get Familiar with Basic Music Notation
Understanding basic music notation is essential for reading and playing violin music. Focus on these key elements:
- Staff: The five lines and four spaces where notes are written.
- Clefs: The treble clef is commonly used for violin music.
- Notes: Learn the positions of notes on the staff and their corresponding finger placements on the violin.
- Rhythms: Understand note values (whole, half, quarter, etc.) and how they relate to timing.
To practice reading music:
- Use Beginner Violin Books: These books often include simple exercises and pieces.
- Practice Daily: Spend a few minutes each day reading and playing notes.
- Play Simple Songs: Start with easy songs that use basic notes and rhythms.
Discover Essential Violin Techniques

Practice Open String Notes and Finger Placement
Starting with open string notes and proper finger placement sets a strong foundation. Here’s how to get started:
- Identify Open Strings: G, D, A, and E are the open strings of the violin. Practice playing each one by drawing the bow across the strings.
- Use Proper Bowing Technique: Hold the bow correctly and ensure it moves parallel to the bridge.
- Practice Open Strings Daily: Spend a few minutes each day playing open strings to develop a consistent sound.
To practice finger placement:
- First Position: Place your fingers on the fingerboard in the first position. The first finger should be on the first tape (if using finger tapes), the second on the second tape, and so on.
- Play Notes on Each String: Start with the G string, place your fingers one at a time, and play each note. Repeat for D, A, and E strings.
- Check Intonation: Ensure each note is in tune. Use a tuner or play along with a piano.
Master the Art of Bowing: From Basic Strokes to Advanced Techniques
Bowing is crucial to producing a good sound. Start with basic strokes and progress to advanced techniques:
- Basic Strokes:
- Detache: Play with separate bows for each note.
- Legato: Play smooth, connected notes.
- Staccato: Play short, detached notes.
- Practice Basic Strokes: Use a metronome to maintain a steady tempo. Practice each stroke on open strings, then with fingered notes.
To advance your bowing:
- Spiccato: Bounce the bow lightly on the string. Start slowly, then increase speed as you gain control.
- Sautille: A faster, lighter spiccato. Practice by playing quick, short notes.
- Collé: Use your fingers to pinch and release the bow for short, accented notes.
Develop Your Vibrato for Expressive Playing
Vibrato adds warmth and expression to your playing. Here’s how to develop it:
- Start Slowly: Place your finger on the string and move it back and forth slowly, keeping the movement controlled and even.
- Use a Metronome: Set a slow tempo and practice vibrating in time with the beats.
- Increase Speed Gradually: As you become comfortable, increase the tempo.
Learn Various Bowing Patterns and Articulations
Different bowing patterns and articulations add variety to your playing. Here are some to practice:
- Slurs: Play multiple notes in one bow stroke. Practice by slurring two, three, and four notes together.
- Hooked Bowing: Play two notes in one bow stroke with a slight separation. Practice on scales and simple pieces.
- Martele: Use a sharp, accented bow stroke for each note. Practice on open strings, then apply to fingered notes.
Build Your Violin Repertoire
Start with Simple Scales and Exercises
Scales and exercises form the foundation of violin playing. Begin with these steps:
- Choose a Scale: Start with simple scales like G Major, D Major, and A Major.
- Use a Metronome: Set a slow tempo and play each note evenly.
- Practice Ascending and Descending: Play the scale up and down, focusing on intonation and smooth transitions.
- Add Variations: Incorporate different rhythms and bowing patterns to make your practice more engaging.
To enhance your practice, include basic exercises:
- Finger Placement Exercises: Place your fingers on the fingerboard in first position, playing each note clearly.
- Bowing Exercises: Practice long, smooth bow strokes and short, detached strokes.
- String Crossing Exercises: Practice moving the bow from one string to another smoothly.
Explore Beginner-Friendly Violin Pieces and Songs
Starting with simple pieces builds confidence and musicality. Here’s how to explore beginner-friendly music:
- Choose Easy Pieces: Select pieces like “Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star,” “Mary Had a Little Lamb,” and “Ode to Joy.”
- Learn the Melody: Play each piece slowly, focusing on accuracy and sound quality.
- Use Sheet Music: Follow the sheet music to learn the notes and rhythms correctly.
To further your progress:
- Play Along with Recordings: Listen to recordings of the pieces and play along to improve timing and musicality.
- Join a Violin Class: Participate in group classes or ensembles to practice playing with others.
- Explore Different Genres: Try pieces from various genres like classical, folk, and popular music.
Learn to Read Music Effectively
Reading music is essential for learning new pieces. Follow these steps to improve your music reading skills:
- Understand the Basics: Learn the notes on the staff, clefs, and key signatures.
- Practice with Simple Songs: Start with easy songs that use basic rhythms and notes.
- Use a Metronome: Keep a steady tempo to develop a sense of timing.
To further improve:
- Sight-Reading Exercises: Practice sight-reading daily with new pieces.
- Clap Rhythms: Clap the rhythms of the music before playing to understand the timing.
- Use Flashcards: Use flashcards to memorize note names and positions.
Practice Regularly to Improve Your Skills
Regular practice is vital for continuous improvement. Here’s how to establish an effective practice routine:
- Set a Schedule: Dedicate specific times each day for practice.
- Warm Up: Start with scales and exercises to warm up your fingers and bow arm.
- Focus on Technique: Spend time on specific techniques like bowing, finger placement, and vibrato.
To make your practice more effective:
- Set Goals: Set short-term and long-term goals to stay motivated.
- Record Yourself: Record your practice sessions to identify areas for improvement.
- Seek Feedback: Take lessons from a qualified teacher and seek feedback on your playing.
Overcome Common Violin Challenges
Playing the violin comes with its own set of challenges. Overcoming these issues involves addressing tuning problems, fixing bowing mistakes, improving left-hand finger independence, and developing consistent intonation.
Address Tuning Issues and Solutions
Tuning the violin can be tricky but is essential for good sound. Here’s how to tackle tuning problems:
- Check the Strings Regularly: Ensure your strings are not worn out or damaged.
- Use a Tuner: An electronic tuner can help you tune each string accurately. Start with the A string and then tune D, G, and E.
- Tune with Pegs: Use the tuning pegs for large adjustments. Turn them gently to avoid breaking the strings.
- Fine-tune with Adjusters: Use fine-tuners for small adjustments. These are usually located on the tailpiece.
For common tuning problems:
- Slipping Pegs: If pegs slip, apply peg compound to increase friction.
- Sticking Pegs: If pegs stick, use a small amount of peg compound or chalk.
- String Stretching: New strings may stretch. Retune frequently until they settle.
Fix Common Bowing Mistakes
Bowing mistakes can affect the sound quality. Here’s how to correct common errors:
- Check Bow Hold: Ensure your fingers are curved naturally, and your thumb is bent.
- Bow Parallel to the Bridge: Keep the bow straight and parallel to the bridge. Use a mirror to check your bowing angle.
- Apply Even Pressure: Avoid pressing too hard or too lightly. Practice long, slow strokes to develop even pressure.
To fix specific bowing mistakes:
- Squeaky Sound: Lighten the pressure and ensure the bow is straight.
- Scratchy Sound: Check the bow hair and apply the right amount of rosin.
- Uneven Sound: Practice with a metronome to maintain a steady tempo and even bow strokes.
Improve Left-Hand Finger Independence
Finger independence is crucial for playing fast and accurately. Here’s how to improve it:
- Finger Exercises: Practice lifting and placing each finger independently. Start slowly and increase speed gradually.
- Scales and Arpeggios: Play scales and arpeggios to strengthen each finger. Focus on keeping fingers close to the fingerboard.
- Finger Tapping: Tap each finger on the table or a hard surface to develop strength and coordination.
To further improve finger independence:
- Finger Patterns: Practice different finger patterns on each string.
- Trills: Practice trills (rapid alternation between two notes) to increase finger speed and strength.
- Etudes: Play etudes specifically designed to improve finger independence and dexterity.
Develop Consistent Intonation
Consistent intonation is vital for a good sound. Here’s how to achieve it:
- Use a Tuner: Practice with a tuner to ensure each note is in tune.
- Listen Carefully: Develop your ear by listening to recordings and playing along.
- Check Finger Placement: Ensure your fingers are placed correctly on the fingerboard. Use finger tapes if necessary.
To maintain consistent intonation:
- Play Slowly: Practice slowly to focus on intonation and finger placement.
- Use Drones: Play along with a drone (a sustained pitch) to improve your sense of pitch.
- Record Yourself: Record your practice sessions and listen for intonation issues.
Find Inspiration and Motivation
Explore Different Violin Styles and Genres
Exploring various violin styles and genres can keep your practice sessions exciting and broaden your musical skills. Here’s how to dive into different genres:
- Classical Music: Start with classical pieces by composers like Bach, Mozart, and Beethoven. These pieces provide a strong foundation in technique and musicality.
- Folk Music: Explore folk traditions from around the world. Try playing Irish jigs, Scottish reels, or Appalachian tunes to develop rhythmic precision and bowing techniques.
- Jazz: Experiment with jazz standards. Learn to improvise and explore different rhythms and scales.
- Pop and Rock: Play popular songs by artists like The Beatles, Coldplay, or Taylor Swift. This genre helps you connect with modern music styles and audiences.
To explore these genres:
- Listen to Recordings: Listen to recordings from various genres to get a sense of their unique styles.
- Play Along: Find sheet music or tabs for songs in these genres and play along with the recordings.
- Experiment with Techniques: Try different bowing patterns, fingerings, and articulations specific to each genre.
Listen to Renowned Violinists for Inspiration
Listening to renowned violinists can provide inspiration and insights into advanced techniques. Here’s how to draw inspiration from the greats:
- Identify Famous Violinists: Start with renowned violinists like Itzhak Perlman, Hilary Hahn, and Joshua Bell. Their performances are examples of mastery and musicality.
- Watch Performances: Watch live or recorded performances. Observe their techniques, stage presence, and musical interpretation.
- Study Their Techniques: Pay attention to their bowing, finger placement, and vibrato. Try to incorporate these techniques into your practice.
To get the most out of this:
- Read Interviews and Biographies: Learn about their practice routines, challenges, and career paths.
- Attend Live Concerts: If possible, attend live concerts to experience the music firsthand.
- Follow on Social Media: Many violinists share practice tips, behind-the-scenes content, and personal insights on social media.
Join a Violin Community or Orchestra
Joining a community or orchestra can provide support, motivation, and performance opportunities. Here’s how to get involved:
- Find Local Groups: Look for local violin groups, orchestras, or music schools that offer ensemble opportunities.
- Participate in Online Communities: Join online forums, social media groups, or virtual ensembles where you can share experiences and seek advice.
- Attend Workshops and Masterclasses: Participate in workshops and masterclasses to learn from experienced teachers and meet other violinists.
To make the most of these opportunities:
- Engage Actively: Participate actively in rehearsals and discussions. Share your progress and ask for feedback.
- Perform Regularly: Take advantage of performance opportunities to build confidence and stage presence.
- Network: Connect with fellow musicians and teachers. These connections can provide support and opportunities for collaboration.
Set Achievable Practice Goals
Setting achievable practice goals helps maintain focus and track progress. Here’s how to set effective goals:
- Define Your Objectives: Determine what you want to achieve. Goals could include mastering a particular piece, improving a technique, or preparing for a performance.
- Break Down Goals: Divide larger goals into smaller, manageable tasks. For example, if you aim to learn a piece, break it down into sections and focus on one section at a time.
- Set a Timeline: Establish a timeline for each goal. This helps create a sense of urgency and keeps you on track.
To stay on track:
- Track Your Progress: Keep a practice journal to record your progress and reflect on what you’ve learned.
- Celebrate Achievements: Acknowledge your achievements, no matter how small. This boosts motivation and confidence.
- Adjust as Needed: Be flexible and adjust your goals as necessary. If you encounter challenges, revise your approach and keep moving forward.
Care for Your Violin

Protect Your Violin with a Proper Case
Choosing the right case is crucial for protecting your violin. Here’s how to ensure your instrument is well-protected:
- Select a Hard Case: A hard case provides the best protection against physical damage. Look for one with a sturdy exterior and a plush interior.
- Check for Secure Fittings: Ensure the case has secure latches and hinges. It should close tightly to keep out dust and moisture.
- Use a Shoulder Rest Compartment: Some cases come with a separate compartment for the shoulder rest, keeping it secure and avoiding pressure on the violin.
To further protect your violin:
- Use a Hygrometer: A hygrometer measures humidity levels inside the case. Aim to keep the humidity between 40-60% to prevent cracking or warping.
- Store Properly: Always store your violin in its case when not in use. Avoid placing it near heat sources or in direct sunlight.
- Transport Carefully: When traveling, ensure the case is secured and cushioned. Avoid leaving your violin in a car for extended periods.
Maintain Optimal Violin Condition
Regular maintenance keeps your violin in optimal playing condition. Here’s how to maintain your instrument:
- Clean the Violin: Wipe down the violin after each use with a soft, lint-free cloth to remove rosin dust and sweat.
- Check the Strings: Inspect the strings regularly for signs of wear. Replace them if they show fraying or become difficult to tune.
- Inspect the Bow: Ensure the bow hair is clean and properly tightened. Rehair the bow as needed.
To maintain your violin’s condition:
- Use a Humidifier: In dry climates, use a violin humidifier to maintain appropriate humidity levels. Insert the humidifier into the F-hole to prevent dryness.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Keep your violin away from extreme temperatures, which can cause the wood to expand or contract, leading to cracks.
- Check the Bridge and Sound Post: Ensure the bridge is upright and correctly positioned. Check that the sound post inside the violin is secure and in the right place.
Learn About Violin Maintenance and Repairs
Understanding basic maintenance and knowing when to seek professional repairs is vital. Here’s how to handle common issues:
- Replace Strings: Learn to replace strings yourself. Loosen the old string, remove it from the peg, and insert the new string, winding it evenly around the peg.
- Adjust the Bridge: If the bridge is not upright, carefully adjust it back into position. Ensure it’s centered between the F-holes and the feet are flat on the top plate.
- Tighten Pegs: If the pegs slip, apply a small amount of peg compound to improve friction. If they are too tight, use a bit of peg soap or graphite.
For more complex repairs:
- Cracks and Open Seams: If you notice any cracks or open seams, take your violin to a luthier for professional repair. Do not attempt to fix these yourself, as improper repairs can damage the instrument.
- Sound Post Adjustments: Adjusting the sound post requires expertise. If it moves or falls, seek a luthier’s help to reposition it correctly.
- Rehairing the Bow: Rehairing a bow is a delicate process best handled by a professional. Take your bow to a luthier for rehairing when necessary.
Conclusion
Taking proper care of your violin and continuously improving your skills are essential for any violinist. Start by learning the basics, such as understanding the parts of the violin, mastering posture, and developing bow hold techniques. Progress by discovering essential techniques, practicing open string notes, and learning vibrato. Build your repertoire with simple scales and beginner-friendly pieces while maintaining consistent practice. Overcome common challenges by addressing tuning issues, fixing bowing mistakes, and improving finger independence. Find inspiration by exploring various violin styles, listening to renowned violinists, and joining communities. Lastly, ensure your violin remains in top condition by using a proper case, maintaining it regularly, and knowing when to seek professional repairs.
FAQs
- How often should I practice the violin?
- Aim for daily practice, even if it’s just 20-30 minutes.
- What should I look for in a violin case?
- Choose a hard case with secure fittings and humidity control.
- How can I improve my intonation?
- Practice slowly with a tuner and listen carefully to each note.
- What genres are good for beginner violinists?
- Start with classical, folk, jazz, and pop.
- When should I replace my violin strings?
- Replace them when they show signs of wear or become difficult to tune.